Did you know ??
Pets may contract multiple diseases from a single tick bite.
There about 850 tick species, some of which are capable of transmitting diseases.
Ticks are arachnids. Meaning, they are more closely related to spiders and scorpions than insects.
What should you know about Ticks ??
- Ticks have four life stages: egg, larva (infant), nymph (immature), and adult (mature).
- Ticks feed on the blood of their host -- humans, birds, reptiles, and wild and domestic mammals.
- Ticks may appear as a small dark speck on your pet's fur.
- Tick infestations are more common in dogs than cats.
- Ticks are generally not born with disease agents. They acquire them during feeding and pass them along onto other animals during subsequent feedings.
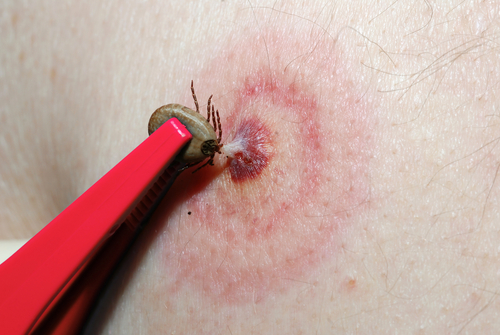
- Never remove a tick with your bare hand. Instead, using tweezers, grasp the tick close to the skin and pull gently.
How do it spread ??
- Depending on the tick species and its stage of life, preparing to feed can take from 10 minutes to 2 hours.
- When the tick finds a feeding spot, it grasps the skin and cuts into the surface.
- A tick will suck the blood slowly for several days.
- If the host animal has a bloodborne infection, the tick will ingest the pathogens with the blood.
- After feeding, most ticks will drop off and prepare for the next life stage.
- At its next feeding, it can then transmit an acquired disease to the new host.
Do ticks transmit disease ??
YES,they do !!!
Babesiosis
- Babesiosis is a protozoan infection that occurs infrequently in Minnesota. Approximately 20% of patients diagnosed with Babesiosis also have Lyme disease from the same black legged tick (deer tick) bite.
Lyme Disease
- Lyme disease is a potentially serious bacterial infection affecting both humans and animals. The incidence of Lyme disease in Minnesota has been increasing in recent years.
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever is extremely rare in Minnesota, but isolated cases have been reported within the state.
Tularemia
- Tularemia is a potentially serious illness that occurs naturally in the United States. It is caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis found in animals (especially rodents, rabbits, and hares). Human cases of tularemia are sporadically reported in Minnesota.
Symptoms
- Walk in the center of the trail to avoid picking up ticks from grass and brush.
- Wear clothes that will help shield you from ticks.
- Use a good tick repellent.
- Check frequently for ticks and remove them promptly.
Did you know ?
Mites are non-hazardous to humans
Mites do not bite and are not vectors of any kind of infection.
Mites live on skin flakes from people and animals and some species also live on flour dust.
What should you know about mites ??
- House dust mites are microscope bugs that primarily live on dead skin cells regularly shed from humans and their animal pets.
- Dust mites are generally harmless to most people.
- They don't carry diseases, but they can cause allergic reactions in asthmatics and others who are allergic to their feces.
- Beds are a prime habitat.
- A typical used mattress may have anywhere from 100,000 to 10 million mites inside.
- Ten percent of the weight of a two year old pillow can be composed of dead mites and their droppings.
Do mites transmit disease ??
- Some mites can transmit (‘vector’) certain microbes that may cause infection and disease.
- The most prominent mite-associated disease is called scrub typhus, and is caused by a rickettsia transmitted by chiggers (larval mites).
- Another disease, rickettsialpox, is far more widespread throughout the world.
- This is caused by yet another rickettsial agent (Rickettsia akari), and is transmitted by the house mouse mite (Liponyssoides sanguineus).
Symptoms
- Hay fever,
- Watering eyes,
- Runny nose,
- Sneezing,
- Asthma, difficulty in breathing.
Prevention and Control